French Bulldogs captivate dog lovers worldwide with their distinctive bat ears, compact bodies, and charming personalities, but it’s perhaps their remarkable variety of coat colors and patterns that truly showcases the breed’s diversity. From the classic brindle to the rare and exotic lilac, blue, and merle variations, Frenchies display a stunning spectrum of appearances that make each dog uniquely beautiful. This comprehensive guide delves into the fascinating world of French Bulldog colors and features, exploring standard and rare variations, explaining the genetics behind these colorations, and providing valuable insights for prospective owners and enthusiasts alike. Whether you’re considering adding a Frenchie to your family or simply admire these delightful companions, understanding their color genetics and distinctive features will deepen your appreciation for one of the world’s most beloved dog breeds.
Understanding French Bulldog Coat Genetics
French Bulldog coat genetics can seem complex, but understanding the basic principles helps explain the stunning variety of colors and patterns you see in these beloved companions. Multiple genes interact to create the distinctive appearance of each Frenchie, from classic brindle to rare lilac.
Color vs Pattern: The Fundamental Difference
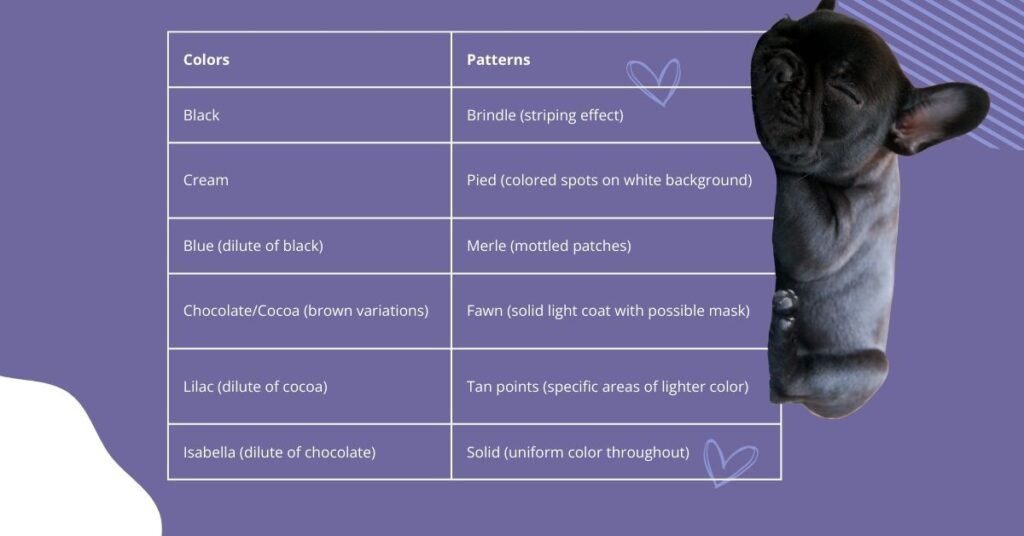
When discussing French Bulldog appearances, it’s crucial to distinguish between colors and patterns. Colors refer to the actual pigmentation of the coat, while patterns describe how those colors are distributed across the dog’s body.
Colors in French Bulldogs include:
- Black
- Cream
- Blue (dilute of black)
- Chocolate/Cocoa (brown variations)
- Lilac (dilute of cocoa)
- Isabella (dilute of chocolate)
Patterns include:
- Brindle (striping effect)
- Pied (colored spots on white background)
- Merle (mottled patches)
- Fawn (solid light coat with possible mask)
- Tan points (specific areas of lighter color)
- Solid (uniform color throughout)
A single French Bulldog can have both a base color and a pattern that works together to create their unique appearance. For example, a “blue brindle” Frenchie has a blue base color with brindle striping.
The Genetic Basis of Coat Colors
French Bulldog coat colors are determined by several genetic loci (specific positions on chromosomes). Each locus contains genes that influence different aspects of pigmentation.
At the most basic level, coat color inheritance follows dominant and recessive patterns. Dominant genes require only one copy to be expressed, while recessive genes need two copies (one from each parent) to appear in the dog’s physical traits.
Key genetic loci affecting French Bulldog coloration include:
- The B Locus: Controls black vs. brown (chocolate/cocoa) pigment
- The D Locus: The dilution gene that creates blue from black or lilac from chocolate
- The E Locus: Controls mask presence and cream coloration
- The A Locus: Determines patterns like solid, tan points, or fawn
- The K Locus: Affects brindle patterning
- The S Locus: Controls the pied/white spotting pattern
- The M Locus: Controls the merle pattern
When breeders understand these genetic principles, they can predict possible coat colors and patterns in puppies. For example, breeding two blue carriers (dogs with one copy of the dilution gene) gives a 25% chance of producing blue puppies.
DNA testing has revolutionized color breeding by allowing breeders to determine a dog’s genetic makeup before breeding decisions are made. This helps avoid undesirable combinations that could lead to health issues, particularly with genes like merle, where doubling can cause serious problems.
Understanding these genetic fundamentals not only satisfies curiosity about why your Frenchie looks the way it does but also supports responsible breeding practices that prioritize health alongside aesthetics.
Standard French Bulldog Colors
French Bulldogs are beloved for their distinctive appearance and charming personalities, with coat colors playing a significant role in their unique appeal. The breed standard recognizes several official and exotic color variations, each with its own distinctive characteristics and genetic background.
Color Genetics and Inheritance

Before diving into specific colors, it’s important to understand that French Bulldog coat colors are determined by complex genetic interactions. The primary color genes responsible for their coat variations include:
- Agouti (A) gene
- Black (B) gene
- Dilution (D) gene
- Merle gene
- Cream (E) gene
These genetic factors interact to create the wide range of colors and patterns seen in French Bulldogs. Responsible breeders carefully consider genetic testing to prevent potential health issues associated with certain color combinations.
Recognized Color Variations
The American Kennel Club (AKC) and breed standards recognize several standard colors:
- Brindle
- Fawn
- White
- Cream
- Pied
- Black
- Black and White
Brindle French Bulldogs
Brindle is one of the most classic and recognized French Bulldog coat patterns. Characterized by a base color with dark striping that resembles tiger stripes, brindle Frenchies showcase a stunning and dynamic coat appearance.
Brindle Variations
- Tiger Brindle: Intense, well-defined dark stripes on a lighter base color
- Reverse Brindle: Dark base with lighter stripes, creating a more subdued effect
- Classic Brindle: Moderate striping with balanced color contrast
Color Development
Brindle coloration becomes more pronounced as French Bulldog puppies mature. Newborn puppies may have subtle brindle markings that become more defined over the first few months of life. The intensity and pattern can continue to develop until the dog reaches full maturity.
Fawn French Bulldogs
Fawn is a warm, solid color ranging from light cream to deep red-brown. This color variation is cherished for its soft, uniform appearance and gentle aesthetic.
Fawn Variations
- Light Fawn: Pale, almost cream-like coloration
- Honey Fawn: Warm, golden-brown shade
- Red Fawn: Deep, rich reddish-brown tone
Masked vs. Maskless
- Masked Fawn: Dark facial mask surrounding the muzzle and eyes
- Maskless Fawn: Uniform color without a distinct dark facial marking
Cream French Bulldogs
Cream is a diluted version of fawn, presenting as a soft, pale coloration that ranges from off-white to light tan. Often mistaken for white, cream French Bulldogs have a distinct warmth to their coat.
Distinguishing Characteristics
- Slightly warmer tone compared to pure white
- Uniform coloration
- Potential slight variations in shade intensity
Black and Black & White French Bulldogs
Solid Black
Solid black French Bulldogs are relatively rare. A true black coat is jet black without any brindle or other pattern markings. Careful breeding is required to maintain this color variation.
Black and White
Black and white French Bulldogs feature a predominantly black coat with white markings. These markings can vary in:
- Location
- Size
- Pattern distribution
Pied Pattern in French Bulldogs
The pied pattern is characterized by white as the primary color with patches of another color distributed across the body.
Pied Variations
- Irish Pied: Minimal colored patches, predominantly white
- Extreme Pied: Larger colored patches with white as the base color
Factors Affecting Color
Several factors influence a French Bulldog’s coat color:
- Genetic inheritance
- Parental color genetics
- Potential color dilution genes
- Age-related color changes
Health Considerations
While coat color is aesthetically important, potential French Bulldog owners should prioritize:
- Breed health
- Responsible breeding practices
- Genetic health testing
- Overall dog well-being
Note: Some color variations, particularly those involving extreme genetic modifications, can be associated with potential health risks. Always consult with reputable breeders and veterinarians when selecting a French Bulldog.
Rare and Non-Standard French Bulldog Colors
While standard colors are beloved, rare French Bulldogs captivate enthusiasts with their unique and extraordinary coat variations. These non-standard colors result from fascinating genetic combinations that go beyond traditional breed coloration.
Genetic Considerations for Rare Colors

Understanding rare French Bulldog colors requires insight into complex genetic inheritance patterns:
| Genetic Factor | Impact on Coat Color |
| Dilution Gene | Responsible for softening base colors |
| Recessive Traits | Creates unique color variations |
| Modifier Genes | Fine-tune color intensity and pattern |
Health and Ethical Breeding
Responsible breeding is crucial when exploring rare color variations:
- Not all rare colors are recognized by breed standards
- Some color combinations may carry genetic health risks
- Ethical breeders prioritize dog health over unusual coloration
- Genetic testing is essential for rare color breeds
Blue French Bulldogs
Blue is one of the most sought-after rare colors in French Bulldogs, characterized by a stunning diluted gray-blue coat. This unique coloration is the result of a dilution gene that modifies the black pigment.
Genetic Background
- Caused by a recessive dilution gene (dd genotype)
- Appears as a soft, silvery-blue coat
- Requires both parents to carry the dilution gene
Health Considerations
Blue French Bulldogs can be prone to specific health challenges:
- Color Dilution Alopecia (CDA)
- Potential skin sensitivity
- Higher risk of coat and skin issues
Chocolate and Cocoa French Bulldogs
Chocolate and cocoa variations represent rare and distinctive coat colors that deviate from standard breed coloration.
Characteristics
- Rich, deep brown coloration
- Varies from light milk chocolate to deep cocoa
- Requires specific genetic inheritance
Genetic Complexity
- Recessive gene combination
- Both parents must carry the chocolate gene
- Often accompanied by unique eye and nose pigmentation
Lilac French Bulldogs
A lilac French Bulldog represents the pinnacle of rare color combinations, created through a complex genetic merger.
Genetic Composition
- Combination of blue and chocolate dilution genes
- Appears as a soft, silvery-lavender coat
- Extremely rare and challenging to breed
Distinguishing Features
- Unique, silvery-purple hue
- Soft, muted coloration
- Requires precise genetic inheritance
Isabella French Bulldogs
Isabella coloration represents another extraordinary rare color variation.
Genetic Makeup
- Combination of blue and chocolate genes
- Appears as a soft, diluted fawn-like color
- Extremely limited genetic pool
Identifying Characteristics
- Soft, muted coloration
- Unique pigmentation
- Rare genetic combination
Merle French Bulldogs
The merle pattern creates a marbled, mottled coat appearance that is both striking and controversial.
Genetic Basis
- Caused by a dominant merle gene
- Creates irregular pigment patches
- Highly complex genetic inheritance
Critical Breeding Considerations
Serious Health Risks:
- Double merle breeding can cause:
- Severe health defects
- Blindness
- Deafness
- Ethical breeders strongly discourage intentional double merle breeding
New Shade and Exotic Combinations
Exotic color combinations continue to emerge through advanced genetic understanding:
Unique Variations
- Triple-dilute coats
- Combinations of blue, chocolate, and cocoa
- Experimental color breeding techniques
Important Caution
While visually stunning, rare colors should never compromise canine health and well-being. Responsible breeding practices must always take precedence over aesthetic preferences.
Tan Point and Other Pattern Variations
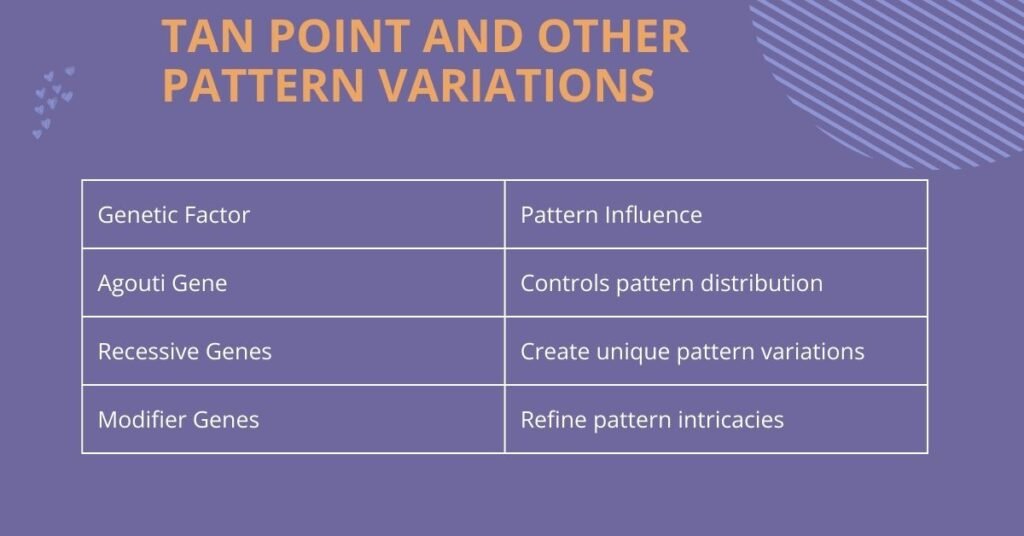
Coat patterns play a crucial role in defining the unique appearance of French Bulldogs. Beyond solid colors, these patterns create intricate and fascinating visual characteristics that make each Frenchie truly one-of-a-kind.
Understanding Coat Pattern Genetics
Genetic inheritance determines the complex patterns and color variations in French Bulldogs:
| Genetic Factor | Pattern Influence |
| Agouti Gene | Controls pattern distribution |
| Recessive Genes | Create unique pattern variations |
| Modifier Genes | Refine pattern intricacies |
Pattern Formation Factors
- Pigment distribution
- Genetic inheritance
- Parental color genetics
- Breed-specific gene variations
Tan Points in French Bulldogs
Tan point is a distinctive genetic pattern that adds depth and complexity to a French Bulldog’s coat. This pattern is characterized by specific tan markings in strategic locations.
Tan Point Characteristics
- Specific tan markings on:
- Eyebrows
- Cheeks
- Chest
- Legs
- Underneath the tail
Color Combinations
Tan point can manifest with various base colors:
| Base Color | Tan Point Appearance |
| Black | High-contrast tan markings |
| Brindle | Subtle tan point highlights |
| Fawn | Softer, more blended tan points |
Genetic Inheritance
- Requires specific recessive gene combination
- Both parents must carry the tan point gene
- Creates a unique and eye-catching coat pattern
Brindle, Pied, and Merle Combinations

Multi-pattern combinations showcase the incredible genetic diversity of French Bulldogs:
Pattern Interactions
- Brindle-Pied: Striped pattern with white patches
- Merle-Brindle: Mottled pattern with tiger-like stripes
- Pied-Tan Point: White base with tan point markings
Combination Characteristics
- Increased genetic complexity
- Unique visual appearance
- Rare and distinctive coat patterns
Solid Pattern in French Bulldogs
The solid pattern represents a uniform coat color without additional markings or variations.
Solid Pattern Genetics
- Controlled by recessive solid gene
- Requires specific genetic inheritance
- Appears as a completely uniform coat color
Genetic Interactions
- Interacts with other color genes
- Can be modified by dilution genes
- Demonstrates the complexity of canine coat genetics
Solid Pattern Variations
- Complete solid color
- Minimal to no pattern variations
- Uniform pigmentation
Coat Features Beyond Color
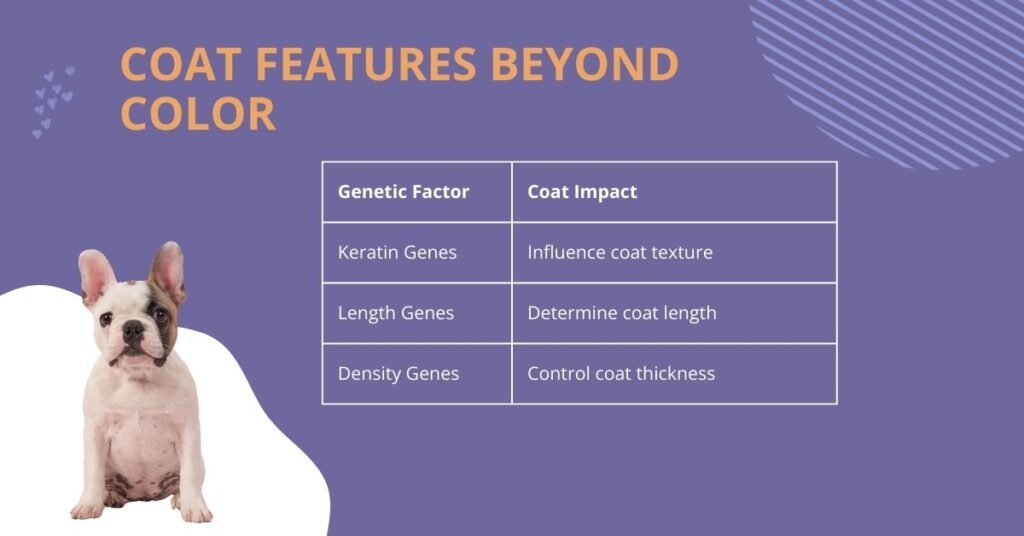
French Bulldogs are more than just their colors – their coat characteristics play a crucial role in their unique appearance and overall health. Understanding these features provides deeper insights into the breed’s genetic complexity and care requirements.
Genetic Influences on Coat Characteristics
Coat features are determined by intricate genetic interactions:
| Genetic Factor | Coat Impact |
| Keratin Genes | Influence coat texture |
| Length Genes | Determine coat length |
| Density Genes | Control coat thickness |
Key Coat Genetic Considerations
- Multiple gene interactions
- Inherited traits
- Environmental influences
- Breed-specific genetic markers
Long-Haired French Bulldogs
Long-haired French Bulldogs represent a fascinating genetic variation that challenges the breed’s traditional short-coat standard.
Genetic Basis
The long-hair trait is controlled by specific recessive genes:
- L1 Gene: Standard short coat
- L4 Gene: Long-hair mutation
Genetic Inheritance
- Requires both parents to carry the long-hair gene
- Extremely rare in the breed
- Considered a genetic anomaly
Characteristics of Long-Haired Frenchies
- Softer, longer coat texture
- Increased grooming requirements
- Unique and distinctive appearance
Long Hair Genetic Specifics
- Recessive inheritance pattern
- Limited breeding opportunities
- Potential health considerations
Coat Texture and Quality
Coat quality is a critical aspect of French Bulldog health and appearance.
Normal Coat Characteristics
- Short and smooth texture
- Tight, close-lying fur
- Minimal to no undercoat
Coat Texture Variations
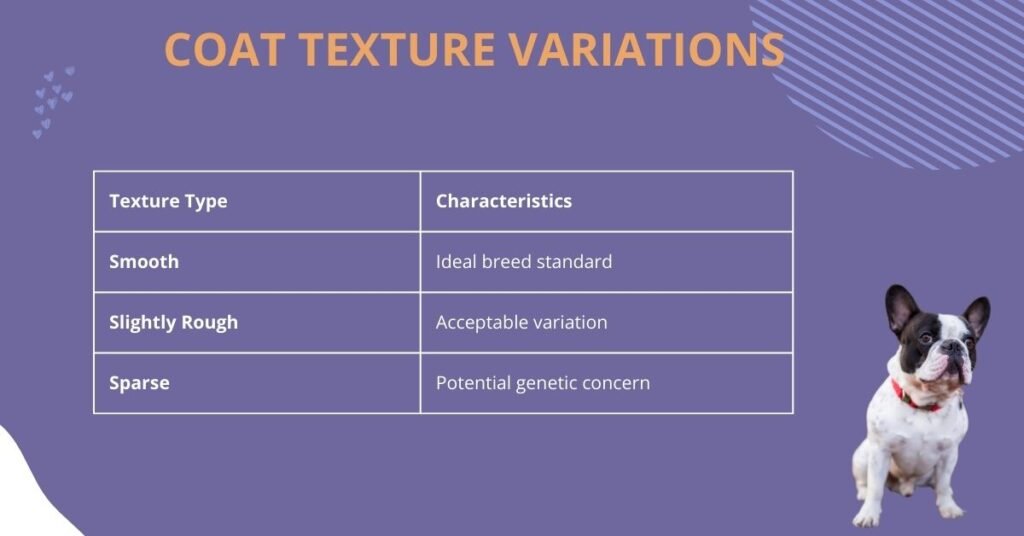
| Texture Type | Characteristics |
| Smooth | Ideal breed standard |
| Slightly Rough | Acceptable variation |
| Sparse | Potential genetic concern |
Grooming Considerations
Essential grooming practices:
- Regular brushing
- Skin fold maintenance
- Attention to potential coat thinning
Factors Affecting Coat Health
- Nutrition
- Genetic predisposition
- Environmental conditions
- Overall health status
Potential Coat Challenges
- Skin sensitivity
- Prone to allergies
- Susceptibility to environmental factors
Comprehensive Coat Care
Coat maintenance is crucial for French Bulldogs:
Holistic Approach
- Regular veterinary check-ups
- Balanced nutrition
- Proper grooming techniques
- Genetic health monitoring
Beyond Appearance: Coat as a Health Indicator
A French Bulldog’s coat is more than just an aesthetic feature:
- Reflects overall health
- Indicates potential genetic issues
- Provides insights into nutritional status
Final Considerations
While coat characteristics are fascinating, responsible owners prioritize:
- Dog’s overall well-being
- Genetic health
- Quality of life
The unique coat of a French Bulldog tells a story of genetic complexity, breed history, and individual characteristics – a testament to the breed’s remarkable diversity.
Health Considerations Related to Coat Color
Coat color in French Bulldogs is more than just an aesthetic feature – it can be intimately linked to potential health considerations. Understanding these connections is crucial for responsible breeding and dog care.
Genetic Color and Health Interactions
The relationship between coat color and health is complex:
| Color Variation | Potential Health Implications |
| Blue | Color Dilution Alopecia |
| Merle | Genetic health risks |
| Extreme Dilutions | Increased susceptibility to skin issues |
Key Genetic Considerations
- Pigment genes impact more than appearance
- Coat color can indicate underlying genetic predispositions
- Not all color variations pose health risks
Color Dilution Alopecia in Blue French Bulldogs
Color Dilution Alopecia (CDA) is a significant health concern for blue-coated French Bulldogs.
Condition Explanation
- Genetic condition affecting diluted coat colors
- Primarily impacts blue and lilac French Bulldogs
- Characterized by:
- Hair loss
- Skin inflammation
- Potential secondary infections
Genetic Mechanism
Dilution gene (d/d genotype) causes:
- Uneven pigment distribution
- Weakened hair follicles
- Increased skin sensitivity
Management Strategies
- Regular veterinary monitoring
- Specialized skin care
- Nutritional support
- Avoiding excessive sun exposure
Merle-Related Health Concerns
Merle pattern carries significant genetic health risks:
Primary Health Challenges
- Hearing impairments
- Vision problems
- Increased risk of congenital defects
Breeding Risks
Double Merle Breeding can cause:
- Severe health complications
- High probability of:
- Deafness
- Blindness
- Neurological issues
Responsible Breeding Practices
- Avoid merle-to-merle breeding
- Comprehensive genetic testing
- Prioritize dog health over coat pattern
General Color-Related Health Myths and Facts
Common Misconceptions
| Myth | Scientific Fact |
| All rare colors are unhealthy | Color alone doesn’t determine health |
| Color determines temperament | No scientific evidence supports this |
| Specific colors are inherently weak | Individual genetics matter most |
Scientific Evidence
Factual Insights:
- Coat color is a complex genetic trait
- Health depends on overall genetic diversity
- Responsible breeding matters more than color
Key Health Determinants
- Genetic diversity
- Responsible breeding practices
- Comprehensive health screening
- Individual dog’s overall constitution
Holistic Approach to Color and Health
While coat color can provide insights, it should not be the sole focus:
Comprehensive Health Considerations
- Regular veterinary check-ups
- Genetic health testing
- Balanced nutrition
- Environmental factors
Empowering Dog Owners
Understanding doesn’t mean fear:
- Be informed, not anxious
- Work with reputable breeders
- Prioritize overall dog health
- Celebrate individual dog’s uniqueness
Final Thoughts
Coat color is just one aspect of a French Bulldog’s genetic makeup. The most important factors remain:
- Responsible breeding
- Comprehensive health care
- Love and proper attention
Every French Bulldog is unique, with their own genetic story that goes far beyond their beautiful coat color.
AKC Standards and Recognition
Breed standards play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and health of French Bulldogs. The American Kennel Club (AKC) provides specific guidelines that define acceptable coat colors and characteristics.
Understanding AKC Color Standards

The AKC recognizes specific color variations for French Bulldogs:
Officially Recognized Colors
- Brindle
- Fawn
- White
- Pied
- Cream
Color Classification Table
| Color Category | Acceptable Variations | Show Ring Status |
| Brindle | Light to dark brindle | Fully Accepted |
| Fawn | Ranging from light to red | Fully Accepted |
| White | Pure white | Fully Accepted |
| Pied | White with colored patches | Fully Accepted |
| Cream | Soft, uniform cream | Fully Accepted |
Reasons Behind Color Restrictions
Historical Context
- Breed preservation
- Maintaining genetic health
- Preventing potential health issues
Color Exclusion Criteria
- Genetic health risks
- Potential breed standard deviations
- Preserving breed characteristics
Non-Standard Color Considerations
- Blue variants
- Chocolate
- Lilac
- Merle
These colors are not recognized in show ring standards due to:
- Genetic complexity
- Potential health concerns
- Deviation from breed’s original characteristics
Show Dogs vs. Pet Quality French Bulldogs
Show Dog Color Standards
- Strict AKC guidelines
- Precise color requirements
- Minimal color variations allowed
Pet Quality Color Variations
- More flexibility
- Broader color acceptance
- Focus on individual dog’s health
Value Considerations
| Color Category | Show Dog Value | Pet Quality Value |
| Standard Colors | High | Moderate to High |
| Non-Standard Colors | Not Accepted | Varies |
| Rare Colors | Disqualified | Potentially High |
Breeding and Color Considerations
Responsible Breeding Practices
- Prioritize genetic health
- Understand color inheritance
- Avoid potential genetic risks
Key Breeding Insights
- Color is secondary to health
- Genetic diversity matters
- Comprehensive health testing
Navigating Color Standards
Potential French Bulldog Owners should:
- Understand AKC guidelines
- Consult reputable breeders
- Prioritize dog’s overall health
- Appreciate individual dog’s unique characteristics
Choosing a French Bulldog Based on Color
Selecting a French Bulldog is an exciting journey that involves more than just choosing a color palette. While coat color can be appealing, it should be one of the least important factors in your decision-making process.
Color Selection Considerations
Factors to Evaluate
- Dog’s health
- Breed temperament
- Genetic background
- Your lifestyle compatibility
Price Variations Based on Color
Color rarity significantly influences French Bulldog pricing:
Color Pricing Breakdown
| Color Category | Price Range | Market Demand |
| Standard Colors | $3,000 – $5,000 | Consistent |
| Rare Colors | $5,000 – $10,000 | High Variability |
| Exotic Variations | $8,000 – $15,000 | Limited Market |
Factors Influencing Price
- Genetic rarity
- Breeder reputation
- Color complexity
- Current market trends
Price Trend Insights
- Blue and lilac colors command premium prices
- Exotic patterns increase value
- Market demand fluctuates
Making the Right Choice
When looking for a Frenchie there must be a lot of factors to consider.
Beyond Color: Holistic Selection Criteria
Critical Considerations:
- Temperament compatibility
- Health history
- Genetic testing
- Breeder reputation
Selecting Your Perfect Frenchie
| Selection Factor | Key Considerations |
| Temperament | Energy level, personality |
| Health | Genetic screening, potential issues |
| Lifestyle | Living space, activity level |
| Color | Personal preference (least important) |
Finding a Reputable Breeder
Red Flags to Avoid:
- No health certifications
- Unusually low prices
- Limited genetic information
- Reluctance to share health records
Positive Breeder Qualities:
- Comprehensive health testing
- Open about genetic background
- Transparent breeding practices
- Prioritizes dog welfare
Financial and Emotional Investment
Understanding True Value
- Companionship matters most
- Color is temporary, personality is permanent
- Long-term commitment is crucial
Practical Advice
- Research thoroughly
- Meet potential puppies
- Consider ongoing care costs
- Prioritize health over aesthetics
Conclusion: The Colorful World of French Bulldogs
The journey through French Bulldog coat colors is far more than a simple aesthetic exploration. It is a fascinating narrative of genetic complexity, breed history, and the remarkable diversity within this beloved breed. From the classic brindle to the rare and exotic color variations, each French Bulldog tells a unique story through its coat – a story of genetic inheritance, health considerations, and individual beauty.
What truly matters is not the specific shade or pattern of a French Bulldog’s coat, but the loving companion that lies beneath. These dogs are defined not by their color, but by their distinctive personalities, their unwavering loyalty, and the joy they bring to their families. Whether you’re drawn to a standard fawn, captivated by a rare blue, or in love with a classic brindle, remember that the most important color is the one that connects with your heart. Responsible ownership, comprehensive care, and understanding the intricate genetic landscape of these remarkable dogs will ensure that your French Bulldog thrives, bringing color and happiness to your life in ways far beyond their coat.

